One of the fundamental lessons of physics is that a stationary charge produces only an electric field, whereas a moving charge produces both an electric and a magnetic field (electro-magnetic field). Electric field and magnetic field are not independent. They are two aspects of the electromagnetic field.
A magnetic force is a force felt near a magnet or alternatively the force felt near a moving current (moving charge). An electric current moving through a conductor behaves like a magnet. A magnetic field is an area where other magnetic materials will feel a force.
Have you ever opened up electronic devices and found copper wires wound on metal?
Magnetic cores are the silent heroes of the modern world. Magnetic materials find a multitude of applications in our daily lives ranging from electricity generation to electricity utilization. These include electric motors, transformers, and generators. They also play a key role in charging and storing equipment in various facets of data storage technology including hard disks and audio cassettes. They are also employed in telephones, CD players, television, loudspeakers, and video recorders.
The magnetic field around a straight wire is not very strong. A strong field can be made by coiling the wire around a piece of soft iron. This electromagnet is sometimes called a solenoid. The shape of the magnetic field is the same as a bar magnet.
The soft iron inside the coil makes the magnetic field stronger because it becomes a magnet itself when the current is flowing. Soft Iron is used because it loses its magnetism as soon as the current stops flowing. Soft iron is said to form a temporary magnet. In this way, the electromagnet can be switched on and off by turning the electricity on and off.
Steel forms a permanent magnet. If steel was used inside the coil, it would continue as a magnet after the electricity was switched off. It would not be useful as an electromagnet. Permanent magnets are needed for electric motors, generators, loudspeakers, and microphones.
The strength of the magnetic field around the coil can be increased by 1. Using a soft iron core (core means middle bit). 2. Using more turns of wire on the coil. 3. Using a bigger current.
Reversing the direction of the current will reverse the magnetic field direction. Alternating current produces a constantly changing magnetic field. An electromagnet is used in the electric bell, relay, circuit breaker, loudspeaker and microphone.
Magnetic cores serve as the backbone of transformers, playing a key role in the efficient transmission of electrical energy. These magnetic cores are typically made from materials with high magnetic permeability, allowing them to concentrate and guide magnetic flux. Common materials include iron and various alloys, each selected for its ability to enhance the transformer’s performance.
The efficiency of transformers is greatly amplified by the presence of magnetic cores. Understanding the working principle involves grasping the concept of magnetic flux — the measure of magnetic field strength passing through a given area. Magnetic cores act as conduits, guiding and intensifying the magnetic flux, which, in turn, facilitates the efficient transfer of electrical energy from one coil to another within the transformer.
What Industries Use Magnetic Components?
Due to their versatility, many businesses and organizations can benefit from these revolutionary components. Industries that use these components the most often include:
- Electronics: Many magnetic components are in electronics like computers and mobile devices. When manufacturers choose the right components, they can dramatically increase power efficiency while also reducing size.
- Appliances: Whether in a fridge or washer at home or advanced industrial appliances for oil rigging, these versatile components play a huge role.
- Automotive: It’s believed that the modern car has more technology than the Apollo 11 rocket that landed on the moon. Key features like climate control, interior and exterior lighting, sophisticated safety programs, dashboard displays, and more require well-regulated voltage.
- Communications: From larger transformers used in advanced telecommunication systems to the cellphone in your pocket, magnetic parts are crucial for successful communication.
- Defense and military: As weaponry, surveillance systems, and transport vehicles become more complex, the more magnetic components become high in demand.
The Two Main Types of Magnetic Components
Although there are several types of magnetic components, they can generally be divided into two major groups: inductors and transformers.
Inductors
An inductor is used to slow down the surges in a current by adding resistance. Some applications include:
- Storing and transferring voltage in power converters
- Choking, blocking, attenuating, or filtering electrical circuit noise
- Creating LC circuits or tuned oscillators
Some common inductors industries often use include:
- Common mode choke inductors: These highly efficient inductors are used to eliminate AC line-conducted common-mode noise when switching power supplies/power supply circuits.
- Input inductors: When handled correctly, an input inductor can provide a low AC ripple current for inputs when switching power supplies—a function that’s useful across many industries.
- Low pass filter inductor: For filtering EMI interference while minimizing signal loss, a Low Pass Filter Inductor is an excellent choice and is the most recommended when dealing with a circuit that has different voltages.
- Toroid inductors and choke inductors: These types of inductors are used in many electronics, including medical supplies, manufacturing equipment, test equipment, and power supplies.
Transformers
A transformer works on the principle of electromagnetic induction, which states that a current-carrying conductor produces a magnetic field around it and vice-versa. A transformer consists of two sets of wires – a primary winding that collects power and a secondary winding that provides power. The primary and secondary windings are wound together on a magnetic iron circuit core, but these coils are not in contact with one another as seen below.
V1 / V2 = N1 / N2 = I2 / I1
- V1: Voltage applied to the transformer primary winding
- V2: Voltage produced at the secondary (load) winding of the transformer
- N1: Number of turns in the primary winding
- N2: Number of turns in the secondary winding
- I1:Current in the primary winding
- I2:Current through the secondary winding
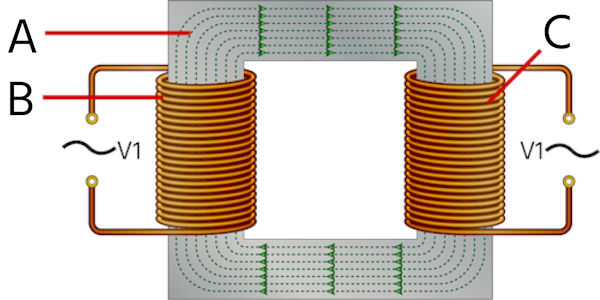
The main role of a transformer is to either increase or decrease voltage levels while stabilizing a circuit’s voltage level. Transformers consist of three major components: a primary coil, a secondary coil, and a core. Just like inductors, there are different types of transformers:
- Flyback: Flyback transformers are in many devices such as computers, electrical pumps, PoE motors, converters and inverters, and AC-DC power supplies.
- Audio transformers: The purpose of audio transformers is to modify signals between different audio applications for a much better overall sound quality. They do this by matching the impedance and voltage of their respective input and output sources.
- Isolation transformers: Isolation transformers are used to isolate electrical devices from their supply line. Due to this unique capability, medical industries often use isolation transformers because they have smaller power losses, can reduce shock administered to a patient, and are compact.
- Power transformers: These types of transformers are often called electrical power transformers and have a wide range of uses. Uses often include induction heating, inverters, having an unregulated power supply, and traction motion control.
Coils
Coils are often used in conjunction with other custom magnetic parts like transformers. A magnetic coil is made from material typically like copper that winds around a cylindrical or toroidal-shaped core. The purpose of a coil is to transmit heat, electricity, or sound. They are used in major industries, including the following:
- Medical
- Electronics
- Telecommunications
- Aerospace and defense
- Automotive
- Commercial manufacturing
In conclusion, magnetic cores are the real parts that move things in this world. In terms of the standard classification of magnetic materials, ferromagnetic materials are mostly used in permanent magnets and data storage applications. Ferrimagnetic materials are employed in the implementation of inductors, transformers, and related magnetic components.
Hope this is useful, thank you.
You may like to read: Introduction to Roblox Scripting, Basics of Microcontrollers, & The Beauty of Circular Primes

