Without PCBs, none of our devices will be able to function. A PCB is the most important platform to connect various components. Whether you’re using a phone or a computer or a television or a washing machine, take some time to understand the printed circuit board (PCB) that is making it possible in the first place.
Prepreg vs. Blank PCB
Prepreg and Blank PCB are not the same and they have different uses in the overall PCB process. Prepreg is nothing more than a layer of insulating material. It is inserted between two cores or between a core and a copper foil to provide the required insulation. On the other hand, blank PCBs or bare PCBs can be basic single-sided boards with copper on one side only or complex multilayer boards with over 32 conductive layers.
Prepreg is the short form for the full word “pre-impregnated” material. Essentially, it refers to the fibreglass cloth that has been impregnated with resin which is used in Burn-IN boards making. The different types of prepreg are FR4 Prepreg, High Tg Prepreg, PTFE Composites, polyamide prepreg, and nonwoven aramid prepreg.
Blank PCB boards form the platform on which all circuit components like processors, capacitors, switches, and chips are assembled. The layered copper interconnects provide the conduction pathways between different components. This allows efficient transmission of power and signals in line with the intended circuit functions.
Blank PCBs offer significant advantages compared to assembling circuits on perf boards or using strip boards for prototyping. Their benefits make blank PCBs integral to modern electronics design and production. Since blank circuit boards can be fabricated according to varied circuit requirements, they provide extensive flexibility.
PCB Core vs. Prepreg
If PCB cores contain copper foil and prepreg, why use prepreg on its own? When designing a board stackup to a desired thickness, the prepreg provides additional thickness without adding unnecessary electrical layers that would become material and process cost adders.
Single sided PCB vs. Double sided PCB vs. Multi sided PCB
A single sided PCB is made from a rigid laminate consisting of woven glass epoxy base material clad with copper on one side of varying thickness. A double sided board is made the same way but with copper on two sides. A multi-layer board is made with one or more inner cores and copper foil in both top and bottom side. Cores could be between 0.038” to 0.005” thick and the number of cores used will depend on the board’s design.
Below video shows a Single Sided PCB with glass epoxy on one side and copper layer on another side. On a side look, the glass epoxy looks like a ceramic tile from the side of a cross section.
Below video shows a Double Sided PCB with copper layer on both sides.
Shapes of Blank PCBs
While blank PCBs usually come in rectangular shape, circular or triangular or customized shapes are not uncommon in usage. Circular blank PCBs are the most common apart from rectangular shaped PCBs.
Glass Epoxy vs. Solder Mask
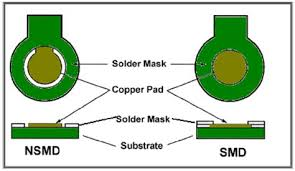
Glass Epoxy forms the PCB core substrate. In both PCB Core and Solder Mask, epoxy is used, however, solder mask is a (typically green colored although not necessary) protective coating of polymer applied on top of the copper (something like powder coating) to prevent oxidation and to prevent short circuits (solder from bridging between closely spaced pads).
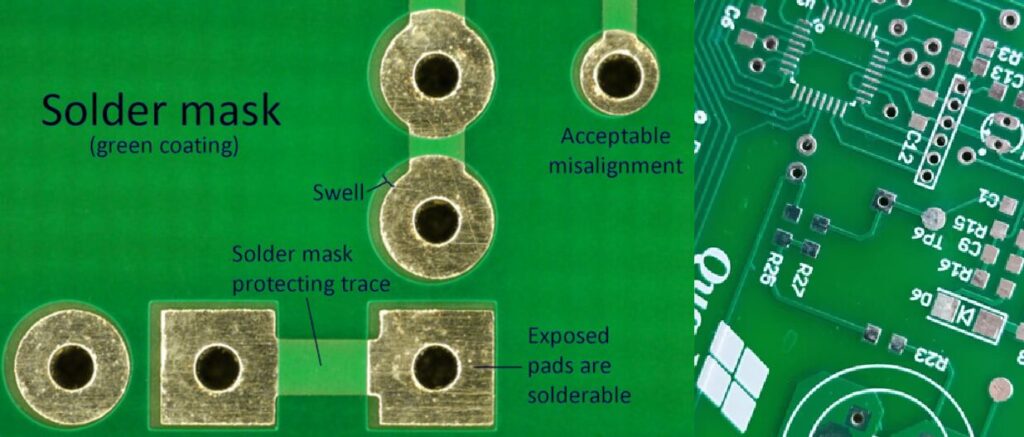
A positive values means that the solder mask will cover a larger area than the copper and a negative value means the solder mask will be smaller than the copper.
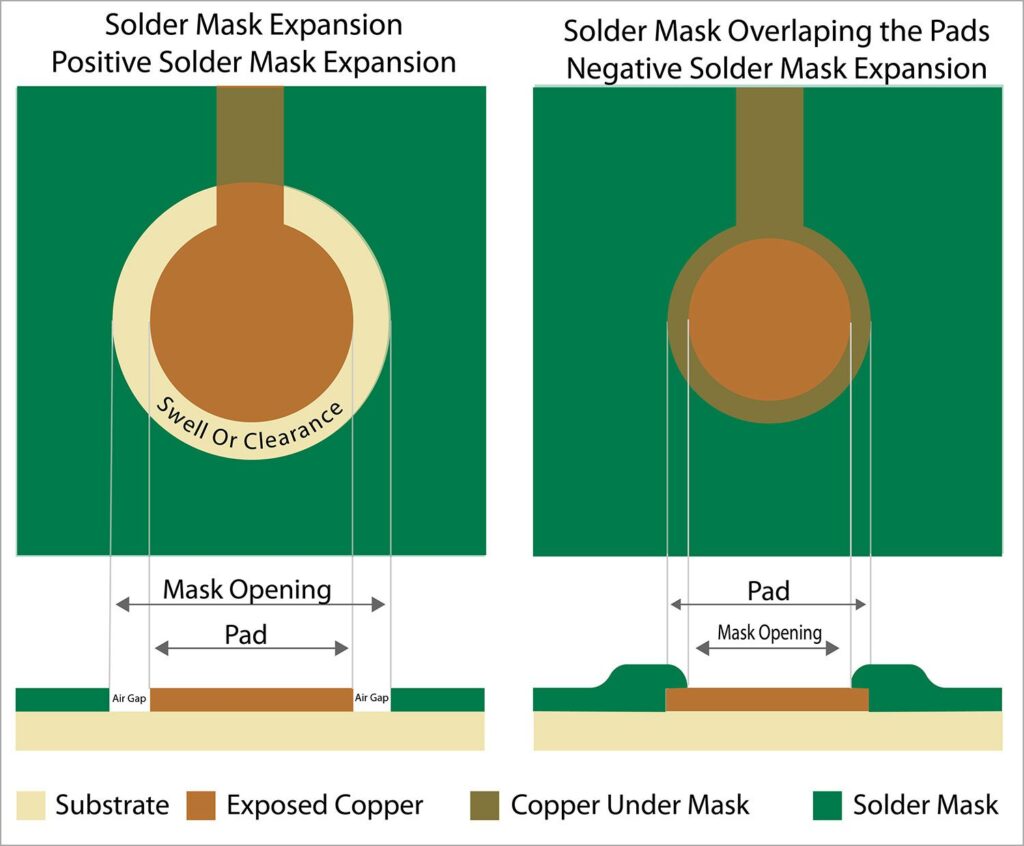
There are different types of solder masks as shown below.
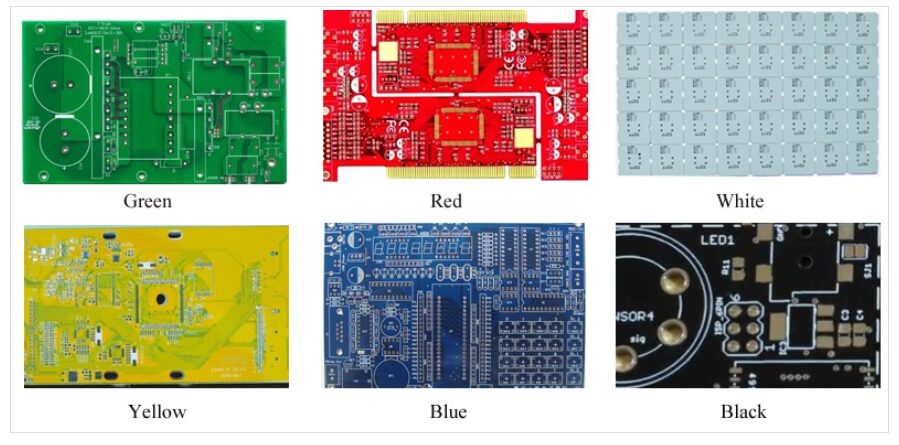
Inside the PCB
Summarizing all the above, the cross section of the inside of a PCB looks like the below.
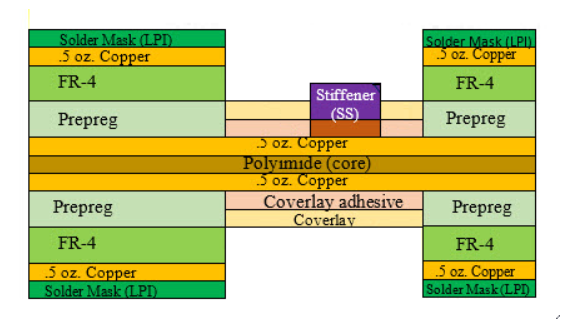
Hope this is useful, thank you.
You may like to read: Is Quantum Computing a Threat to Encryption?, Arduino vs. Raspberry Pi vs. Jetson vs. Microbit, & The Clock Cycle of a CPU