Introduction to Electroplating
Electroplating is a process by which a thin coating of one metal is applied to another base metal by passing the current. This process improves the look of the base metal and provides it protection against rusting and deterioration due to weather. This process is based on electrolysis.Here’s Khan Academy’s video on Electrolysis.
Video of Real Brass Electroplating on steel
In this video, a steel pipe and a steel bowl is coated with brass layer using electroplating or it is commonly called as plating in the furniture industry. The steel is dipped and the brass layer is plated on the steel in 3-5 minutes time. So, all that looks like brass or gold is not brass or gold. Be careful!
Electroplating of Brass on Mild Steel in Reality
Electrolysis:
This process of electrolysis enables the flow of ions (charged particles). But, is a flow of ions actually current flow because I always thought it is the flow of electrons that is the flow of current. So, whatever material you want to coat with copper you will have to put that on the cathode and the copper material will be the anode. Similarly, if you want to do gold plating, then anode will be gold and cathode will be whatever stainless steel material that you want to plate with a layer of gold.
Clarification Point:
Electric current is primarily defined as the flow of electric charge. In most conductive materials, such as metals, this charge is carried by electrons, which flow from the negative terminal to the positive terminal of a power source. Therefore, in the context of metallic conductors, electric current is indeed the flow of electrons.
However, in other contexts, such as in electrolytes or plasma, electric current can also be carried by ions. In these cases, positive ions flow toward the negative terminal, and negative ions flow toward the positive terminal.The flow of ions is also a flow of charged particles, and hence it becomes electric current.
In conclusion, electric current can refer to the flow of electrons in conductors and the flow of ions in electrolytes or gases.
Steps to follow using the “Electroplating Kit for Kids”
The kit consists of one beaker, one zinc plate, one copper plate, one battery snap, one Copper Sulphate salt packet to make the salt solution or the electrolyte solution, one sandpaper to brush off the copper deposited on the zinc plate if you want to repeat the experiment, and one foam piece that acts as a holder.
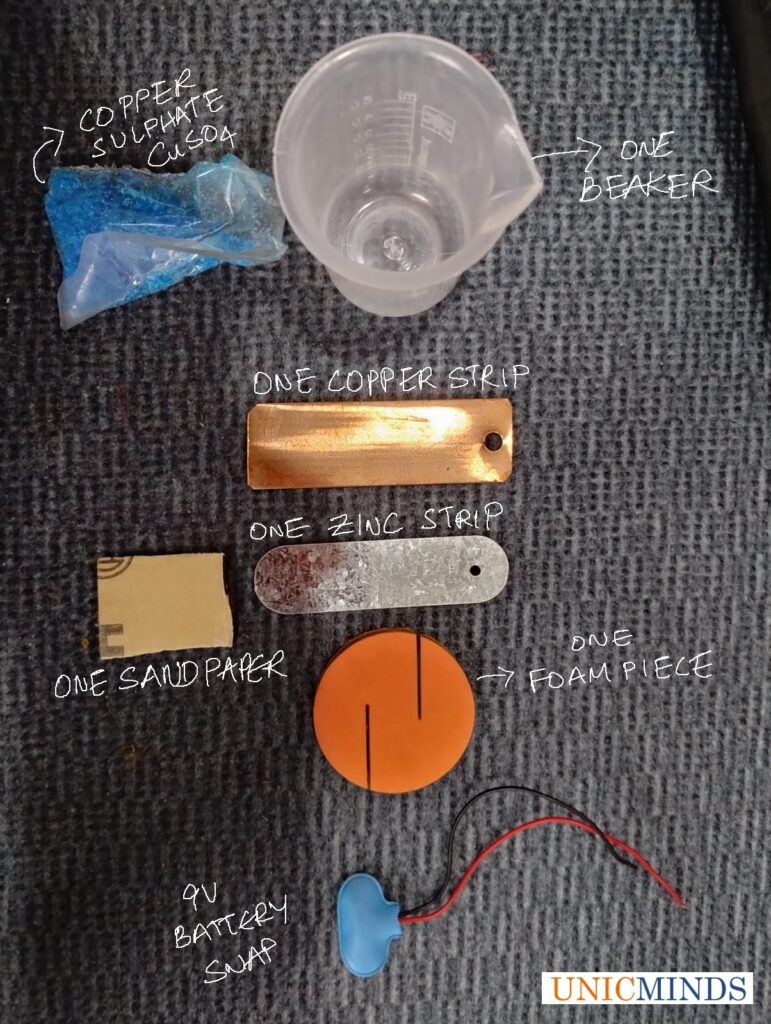

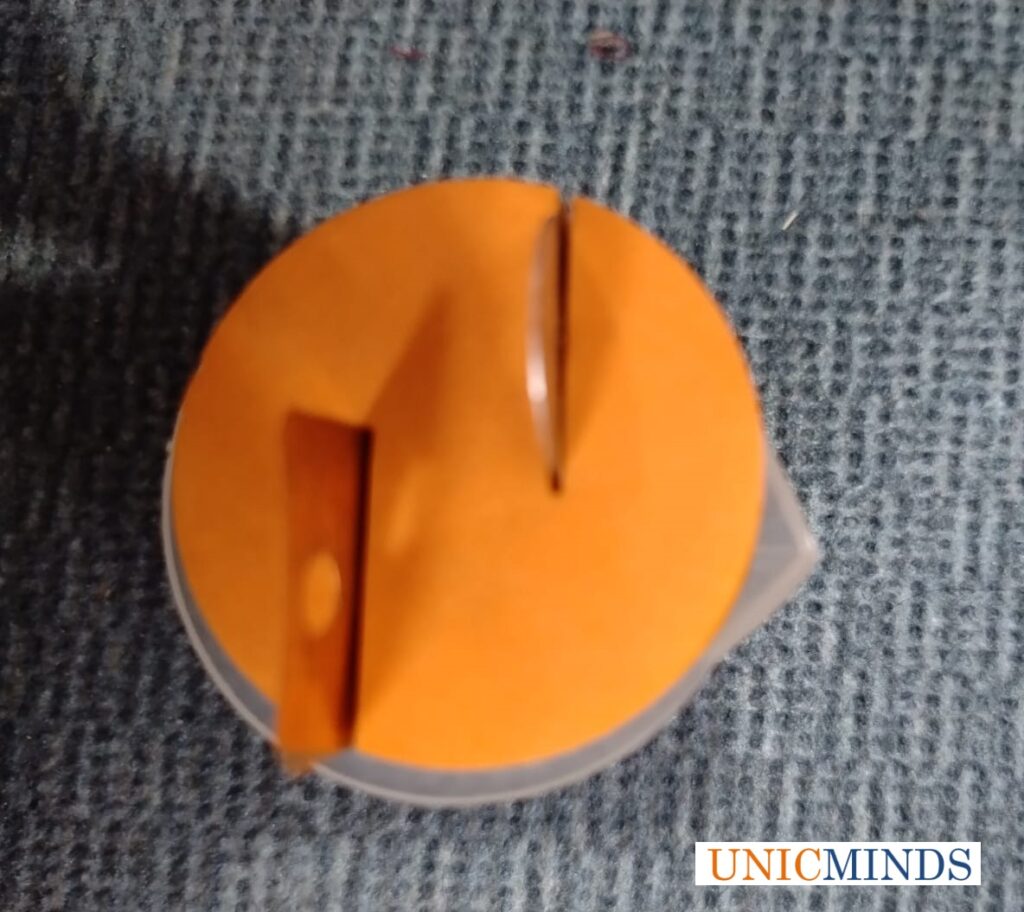
Step 1: Take a foam piece, zinc plate and copper plate. Insert the zinc plate and the copper plate in the groove of the foam piece by pushing it along the grooves as shown below..

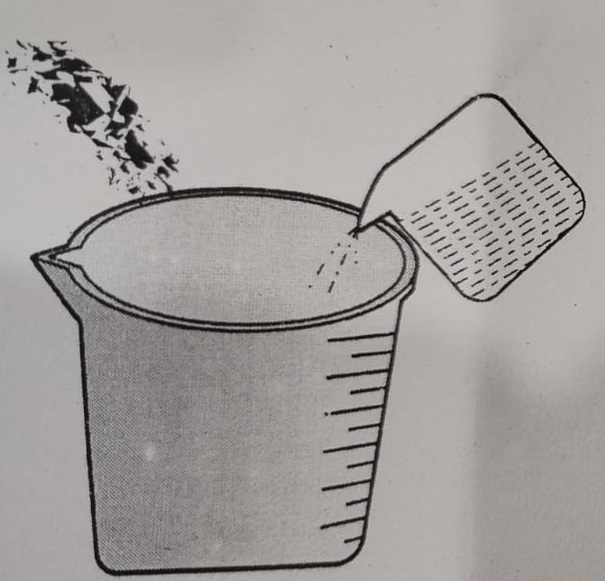
Step 2: Now, take the plastic beaker and put some water and copper sulphate and make the salt solution.

Step 3: Now put the foam piece along with the metal (copper and zinc) plates into the liquid beaker..
Step 4: Now connect the battery snap’s one wire one end with the copper strip and second end of wire with the zinc strip as shown below.
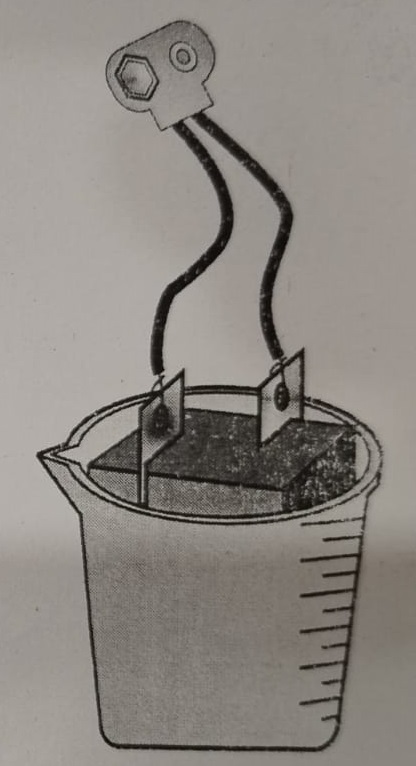
Observations & Results:
After a few minutes, you’ll see that a fine layer of copper gets deposited on the zinc strip. When the zinc strip is copper plated completely, remove it and wash it with water.
Hope this is useful, thank you.
You may like to read: Understanding Object Movements in Unity, Teaching with Humor, & Why Teach Number Theory to Kids?

